What type of laser is used in a Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) system?
Description:The Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) system utilizes a single-frequency laser with a linewidth below 3 kHz and an optical power of 10 mW to 20 mW.
Applications: Fiber Optic Sensing
Tags:DAS Distributed Acoustic Sensing Ultra-Narrow Bandwidth Lasers
The operating principle of the Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) system involves detecting interference between the reference light and the backscattered light from the fiber. This process relies on Rayleigh scattering, necessitating a laser with a linewidth below 3 kHz. The narrower the linewidth, the more effective the system becomes.
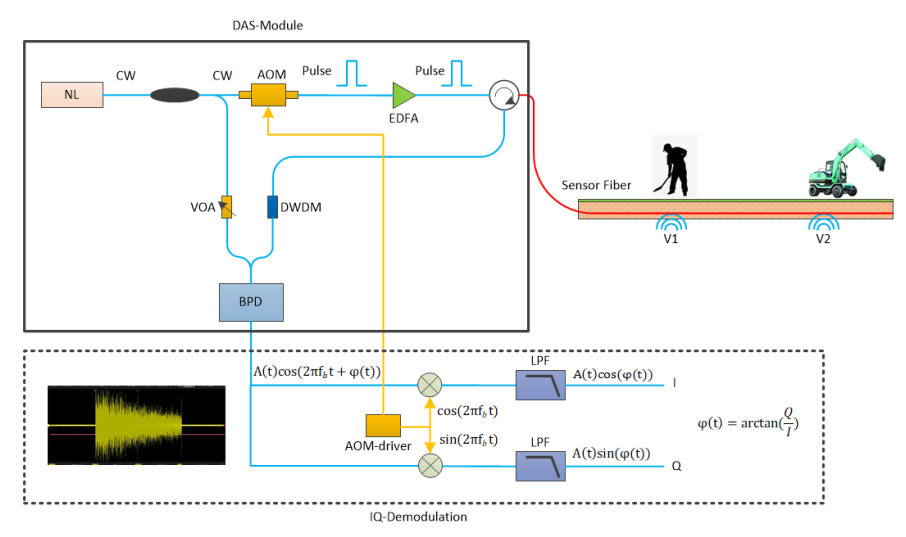
This diagram illustrates the principle of distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) using fiber optics, where NL denotes a narrow-linewidth laser.
We have developed two models for distributed fiber optic acoustic sensing DAS systems: UNL-1550nm-3k-20mw and UNL-1550nm-1k-10mw.
The table below compares the key parameters of these two models, both of which are highly suitable for DAS systems.
| Model No. | Output Type | Wavelength | LineWidth | Power | Product |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UNL-1550nm-3k-20mw | CW | 1550nm | <3kHz | 20mW | Link |
| UNL-1550nm-1k-10mw | CW | 1550nm | <1kHz | 10mW | Link |

Software interface for distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) using ultra-narrow linewidth lasers.